industrial automation
industrial automation
Industrial automation is the use of control systems, such as computers or robots, and information technologies for handling different processes and machinery in an industry to replace a human being. It is the second step beyond mechanization in the scope of industrialization.

Advantages of Automation
- Optimum efficiency
- Low wastage
- Ease in handling
- Greater precision
- Reduction in labor costs
- Increased productivity
- Reduction in the risk of exposure to production hazards
Applications of automation
Discrate
- Automotive
- Food Mfg
- Consumer goods
- Building automation
- Defense
- Parking systems
- Construction
Batch
- Pharma
- Beverage
- Dairy
- Suger
Process
- Mining
- Chemical
- Water Treatment
- Oil & Gas fields
- Power Plants
- Petrochemicals
- Pulp and paper
Automation Devices
PLC
A programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a digital electronic device that uses a programmable memory to store instructions such as logic, sequence, timing, counting, and arithmetic operations to control machines and process.

SCADA
Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) is a system of software and hardware elements that allows industrial organizations to:
- Control industrial processes locally or at remote locations
- Monitor, gather, and process real-time data
- Directly interact with devices such as sensors, valves, pumps, motors, and more through human-machine interface (HMI) software
- Record events into a log file
SCADA systems are crucial for industrial organizations since they help to maintain efficiency, process data for smarter decisions, and communicate system issues to help mitigate downtime.

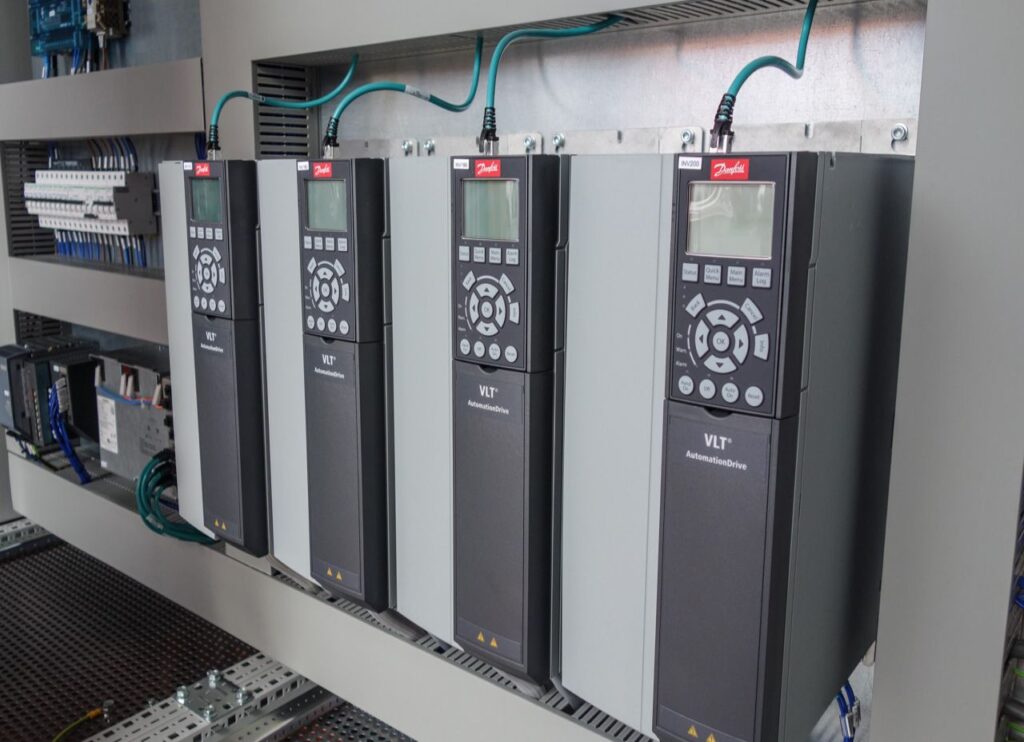
VSD/VFD
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is a type of motor controller that drives an electric motor by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to the electric motor. Other names for a VFD are variable speed drive, adjustable speed drive, adjustable frequency drive, AC drive, Microdrive, and inverter.
Frequency (or hertz) is directly related to the motor’s speed (RPMs). In other words, the faster the frequency, the faster the RPMs go. If an application does not require an electric motor to run at full speed, the VFD can be used to ramp down the frequency and voltage to meet the requirements of the electric motor’s load. As the application’s motor speed requirements change, the VFD can simply turn up or down the motor speed to meet the speed requirement.

